TL;DR
AI assistants don’t just remember, they act. With memory, they keep context from past interactions; with actions, they get work done. Connected through external integrations, assistants can update CRMs, log tasks, send invoices, and pull data on demand. Platforms like Invent make this seamless by combining memory, automation, and real-time data so your assistant feels more like a teammate than a chatbot.
What is AI Memory in the Context of Data and Actions?
Unlike passive storage, AI memory actively powers decisions, telling the assistant which data matters, when to use it, and what to do next. This approach creates continuous, data‑aware workflows, where assistants and chatbots can both recall user context and execute automated processes.
What are actions?
Actions are specific automated tasks by the AI in response to user requests or system logic. They transform user intent into tangible operations, such as creating a record, sending data, or starting an automation, as the following examples:
- Call Zapier MCP Tool
- Update Order on Shopify
- Search Page on Notion
- Create contact on Hubspot
- Create Payment link through Stripe
Memory = context + decision history
Actions = execution based on that learned context (from instructions and user input)
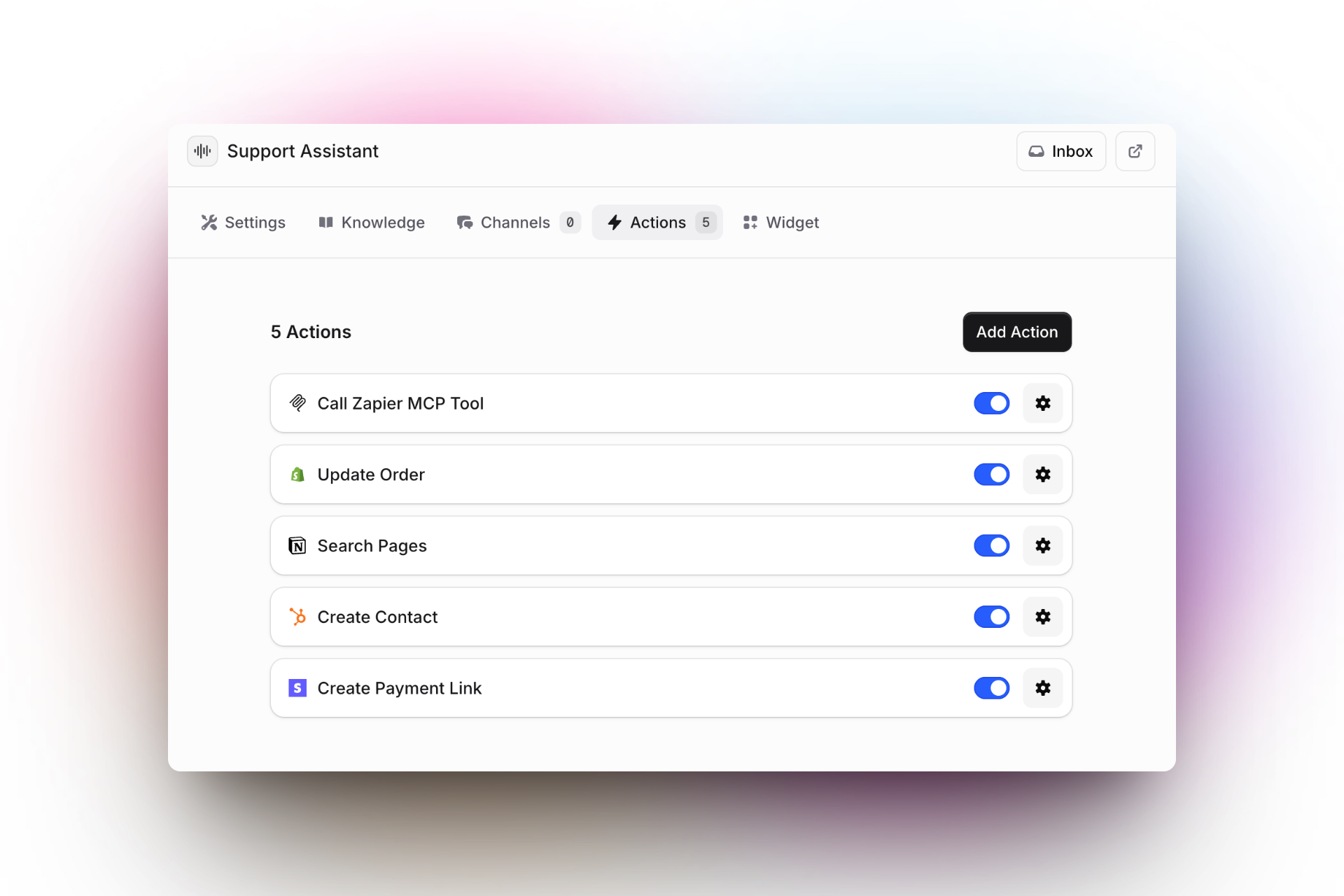
Support Assistant in Invent with 5 configurable actions enabled, letting you automate tasks by integrating tools like Zapier, Shopify, Notion, HubSpot, and Stripe from a single dashboard.
Why data‑driven Memory matters for AI Assistants
Memory transforms chatbots from static tools into operational Assistants capable of handling tasks. With connected memory and external access, they can:
- Pull or update live data (CRMs, Notion, Airtable and more)
- Automate business workflows (bookings, invoices, reminders and more)
- Maintain continuity across sessions
- Provide detailed summaries or reports
This evolution makes an assistant not only knowledgeable but actionable, serving as the operational layer between your instructions and your business data.
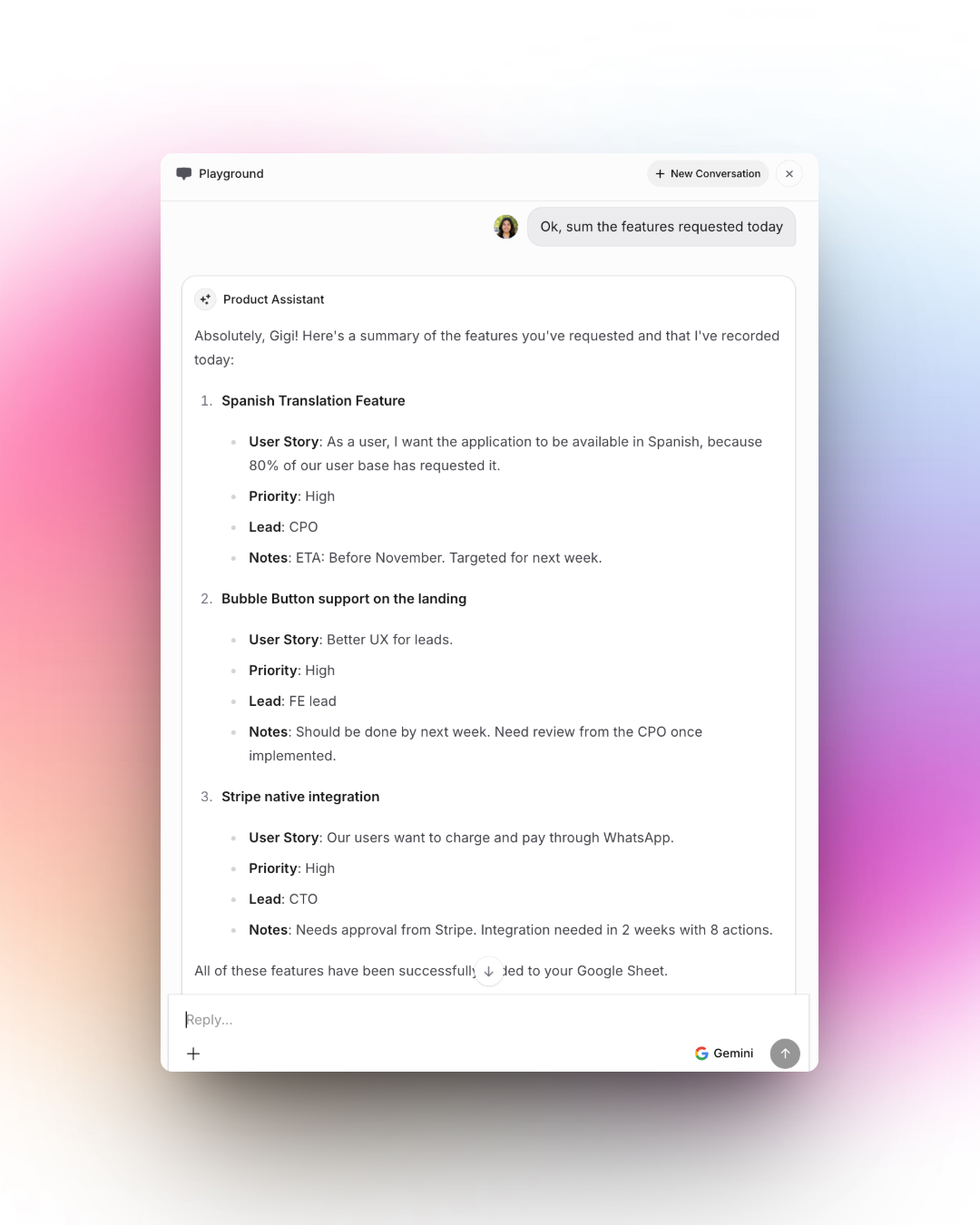
A Product Assistant summarizes today’s requested features, Spanish Translation Feature, Bubble Button support on the landing, and Stripe native integration, detailing each with user stories, priority, leads, and important notes for tracking progress.
AI Memory types with a data focus
AI frameworks organize information across active, stored, and procedural layers.
Short‑Term (In‑session context)
Works like a cache to track current‑session variables, such as running totals or features added during an active chat. Example: “List all features I submitted today”, the AI can calculate and summarize instantly.
Procedural memory
Enables assistants to execute methods repeatedly across similar workflows, a form of automated habit. Example: "Each time you update a client update on Zoho, you should sync status across Notion automatically"
Long‑Term or external data Memory
Stores structured summaries or logs via integrations, helping the AI retrieve knowledge even weeks later.
Example: “Show me the last 5 record saved in Airtable.”
By combining these layers, AI assistants manage live data, perform tasks, and learn from the outcomes, feeding each loop back into the next interaction.
External data and action integrations
AI assistants extend their “memory” through integrations, acting as command centers connected to multiple tools.
How it works
- The AI calls external APIs or native integrations
- Retrieves or updates structured data in real‑time
- Writes summaries back to these systems automatically
Common Actions
- “Update client details in Zoho CRM”
- “Add this deal to Airtable and mark it ‘in progress’”
- “Send Gigi Hamilton Stripe invoice”
On Invent, integrations are native, no API keys needed. Simply connect, choose modules or tables, and the system auto‑fills data fields dynamically.
Note: You need to add all these actions first through the native integrations under Invent. No API keys needed, just need to connect your account and select the tables, modules, details. Select Auto to let AI Auto-fill the value.
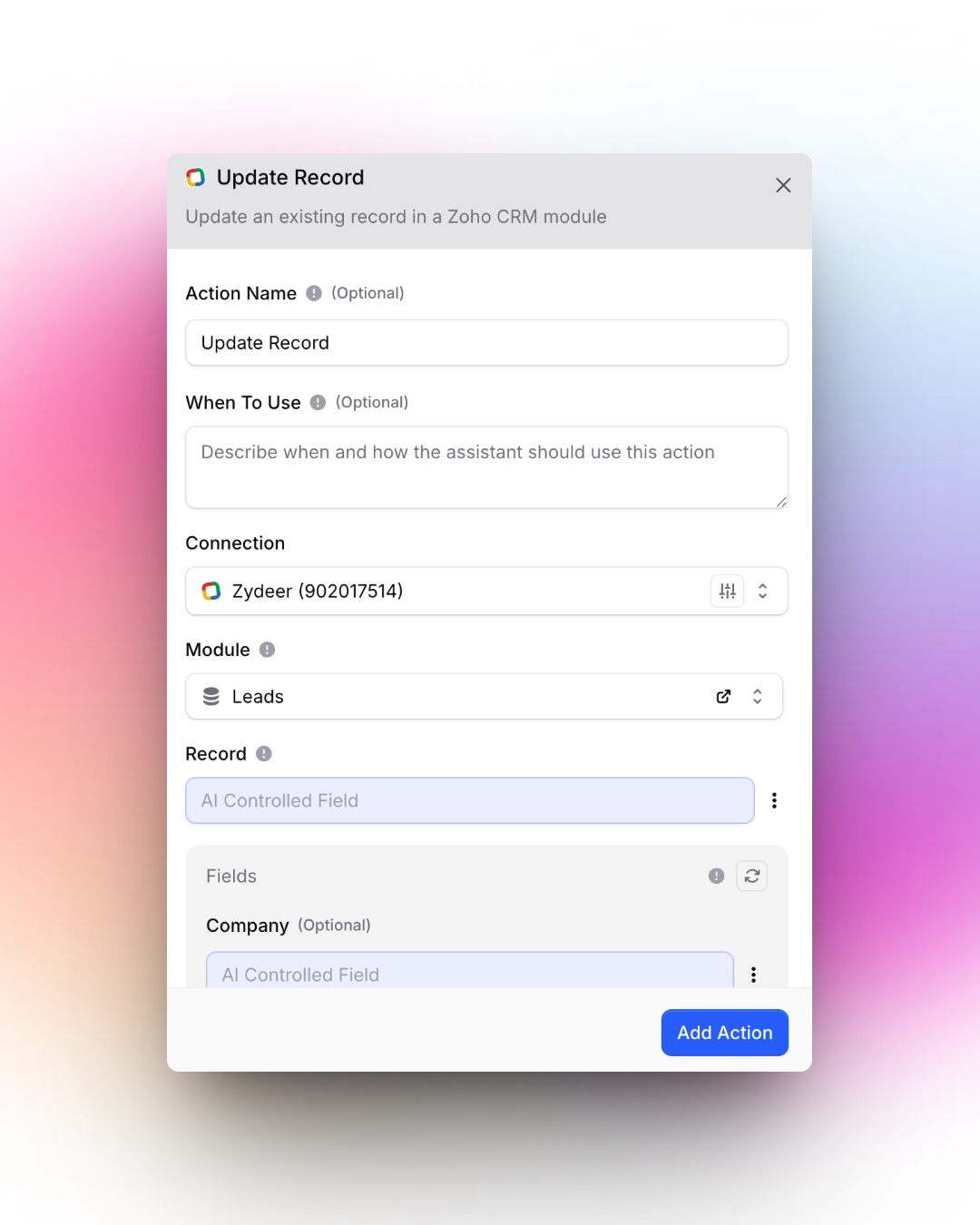
Configure an action from Invent Assistants to update records in a Zoho CRM module using Invent. Specify connection, module, record, and detailed field information to tailor how your assistant can update CRM data.
Best practices for data Actions
To optimize your assistant for accurate, secure workflows:
- Define system instructions for repetitive data actions
- Use triggers on Instructions aka System Prompt: “When I say ‘update’ record, use Zoho actions”
- Ask for summaries for transparency and verification "Will update a, b and c, is that correct?"
- Ensure user approvals for sensitive write‑back actions "Ask for security and confirmation before actions"
This turns AI chat into a verifiable automation channel, combining conversational intelligence with workflow precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the difference between AI memory and data storage?
Memory enables contextual use of data (for reasoning or actions), while storage simply preserves data. Memory is active; storage is passive.
2. How do data integrations improve chatbot intelligence?
They enable real‑time access to live systems (CRMs, spreadsheets, APIs), turning chatbots into task assistants rather than static responders.
3. Can users control which actions AI performs?
Yes. Users can approve, restrict, or automate specific actions through permissions and conversation‑based confirmation prompts. It's also important to name the actions on the Instructions aka System Prompt. Also you'll be able to enable of disable "Auto" for each one of the fields under Actions. You can choose from "Auto", "Manual" and "Selector" if available. Options may vary.
4. How secure is external data access?
Platforms like Invent follow SOC 2 compliance. All retrieval and write actions use encrypted connections and per‑account authorization.
5. How does Invent handle persistent context?
Invent maintains short‑term task state and connects to user‑approved data sources for ongoing recall, summarization, and seamless action recovery across sessions.
Try smarter conversations with Invent
Explore Invent AI Assistants, and see how actions boost every conversation.







